In the dynamic landscape of modern business, data has emerged as a cornerstone of success, driving innovation and informing decision-making. Yet, the mere accumulation of data is not enough; organizations must develop the capabilities to leverage its full potential.
This is where the concept of data maturity comes into play, helping organizations evolve from basic data usage to strategic data management practices and providing a significant competitive advantage. Assessing their position on the data maturity scale is crucial for organizations to identify gaps relative to their industry and define a long-term data strategy that drives sustainable growth.
In this article, we introduce a holistic data maturity assessment framework designed by Artefact to guide organizations in their data transformation. We detail the benefits and key components of our approach, as well as our convictions and lessons learned to make this exercise an organization-wide success.
Understanding data maturity
Data maturity refers to the spectrum of capabilities and practices within an organization, encompassing data collection, storage, processing, analysis, utilization and data governance, to discover actionable insights and drive strategic outcomes.
At the initial stages of data maturity, organizations typically exhibit rudimentary data approaches and fragmented data silos, where data is stored in disparate systems with limited management and usage. As they advance along the maturity scale, they establish quality standards and procedures, enhance data integration capabilities, develop advanced ML/AI use cases, implement robust data governance frameworks to comply with regulatory requirements, and ultimately create an organizational culture of data-driven decision-making.
Data maturity holds significant implications for businesses, allowing them to unlock the full potential of their data assets and shape a sustainable future in the digital age. Organizations with advanced data maturity practices are better equipped to respond to changing market dynamics and customer needs, and to stay ahead of their competition.
Why is data maturity assessment important?
Assessing the data maturity of an organization is crucial, as it empowers the organization to build a long-term data strategy that is fully aligned with its corporate strategy. It also helps define a target data vision and a concrete roadmap to advance data management capabilities. Aligning data efforts with strategic goals ensures that data initiatives contribute directly to achieving organizational objectives, driving growth, and fostering innovation.
As such, the Data maturity assessment should be performed through a comprehensive framework that covers all core aspects of data management in a structured approach. This provides organizations with clear insights into their current data capabilities, highlighting strengths and weaknesses. By understanding where they stand on the data maturity continuum, they can identify areas for improvement and prioritize initiatives efficiently.
A data maturity assessment also allows organizations to benchmark their data positioning against industry standards and best practices, and to prioritize opportunities for differentiation and improvement. By learning from industry leaders and adopting proven strategies, organizations can accelerate their own journey toward data maturity and stay ahead of the curve.
Just as an individual seeks the expertise of a specialist doctor for a comprehensive health check-up, organizations can benefit from engaging data experts like Artefact to successfully conduct their data maturity assessment. Artefact brings unparalleled expertise and methodologies to the table and, more importantly, provides valuable external perspectives and depth to the assessment process, uncovering insights that may have been overlooked internally.
The data maturity assessment framework
Artefact has defined a comprehensive data maturity assessment framework that can be customized for the specific context of each organization to accommodate its data and digital ecosystem. This framework provides a structured approach to evaluate and enhance organizations data management practices across 6 core dimensions, each essential for maximizing the potential of data and driving strategic initiatives.
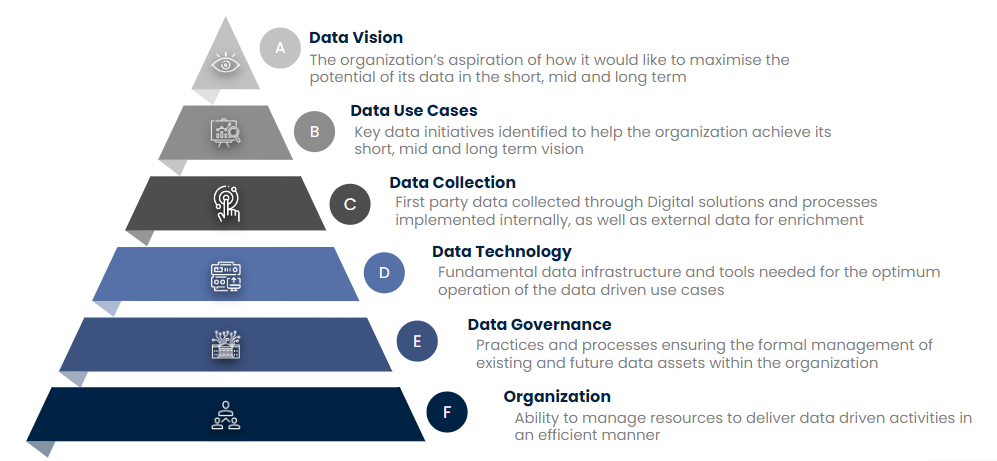
1 – Data vision
Reflects the organization’s aspiration for how it intends to leverage data in the short, mid, and long term. This dimension focuses on the strategic direction and goals related to data usage.
Criteria Assessed:
2 – Data use cases
These are key data initiatives supporting the organization’s vision. This dimension ensures that use cases are purposeful and aligned with strategic goals.
Criteria Assessed:
3 – Data collection
A dimension referring to the different types of data collected by the organization to enable the use cases, including first party data captured through internal digital processes and solutions, and 2nd and 3rd party (external) data used for enrichment.
Criteria Assessed:
4 – Data technology
This dimension encompasses the infrastructure and tools required to efficiently support data integration and use case development, ensuring robust and scalable data operations.
Criteria Assessed:
5 – Data governance
It includes the practices and processes ensuring the formal management of current and future data assets.
Criteria Assessed:
6 – Organization
Refers to the ability of the assessed organization to manage resources efficiently to support data-driven activities.
Criteria Assessed:
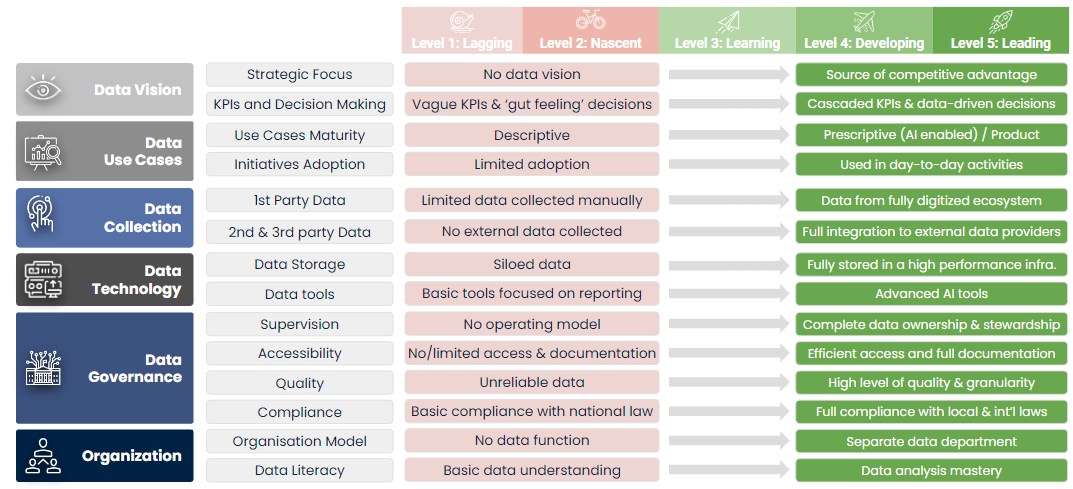
As part of this holistic framework, each criterion within the six dimensions is defined on a scale from 1 (Lagging) to 5 (Leading). Through the assessment, the organization can determine its rating for each specific criterion according to the framework definitions, enabling it to objectively pinpoint any capability gaps compared to key players in their industry.
Artefact convictions for successful assessments
At Artefact, we have developed strong convictions regarding the assessment of data maturity, based on our extensive experience in the fields of data and AI. Here, we outline essential principles and best practices to help organizations to ensure that their assessment process is successful and lays the foundation for long-term, transformative growth.
1 – Consider data maturity assessment an organization-wide initiative
Assessing data maturity should involve a majority of departments across the entire organization, typically including core functions such as Data & IT, Strategy, Operations, Marketing and Sales, Finance, Procurement, HR, and Legal. Since departments interact with data in unique ways, it is essential to conduct interviews with key stakeholders to capture their current challenges and data aspirations. Additionally, explore the department’s value chain to identify how data can overcome existing limitations.
2 – Clearly define levels of maturity from the start
To ensure an objective assessment, levels of maturity should be defined for each criterion and agreed upon early with relevant stakeholders. The findings of the assessment, represented by ratings from 1 to 5 for each assessed criterion, can then be clearly summarized into a representation of the organization’s data maturity. Each rating is backed by a rationale to provide objective and evidence-based reasoning to justify the score.
3 – Focus on identifying gaps and tailoring initiatives
The primary goal of the assessment should be to identify gaps in data management areas where the organization falls short of industry best practices and to develop priority initiatives tailored to address the organization’s unique needs and challenges. This targeted approach ensures that improvement efforts are focused and effective.
4 – Gamify the process to customize outputs for each department
Assessment results should reflect the specific context and needs of each department. One innovative approach we advocate at Artefact is to gamify the assessment process. Gamification involves integrating elements of game design, such as scoring systems, leaderboards, challenges, and rewards. This makes the evaluation much more interactive, encouraging departments to participate actively and to strive for higher data maturity levels.
5 – Set ambitious yet realistic targets
The data maturity framework should establish future goals that are both ambitious and achievable by the organization. Thanks to the assessment, the organization is equipped to develop a clear data vision and strategy that aligns with the organization’s business goals and addresses identified challenges. An action plan should be defined to achieve the vision and is split into three types of objectives:
6 – Promote a culture of data literacy and communicate value
Educating employees across all levels about the importance of data and how to use it effectively fosters a more data-driven organization and supports the journey towards higher data maturity. Demonstrating how improved data practices can enhance decision-making, operational efficiency, and strategic advantage helps secure buy-in and support across the organization.
7 – Continuously Monitor and Adapt
Data maturity is not a one-time assessment but an ongoing journey. Organizations should regularly monitor progress against set targets, adapt corporate and data strategies as needed, and keep pace with technological advancements and evolving business needs.
Conclusion
In summary , conducting Data Maturity Assessment is vital for organizations to shape their long-term data strategies that fit business goals in today’s data-driven world. Partnering with a Data expert like Artefact speeds up the journey towards data maturity by providing an objective and insightful evaluation. We encourage all organizations to embrace this framework to unlock the full potential of data and achieve sustainable growth.

 BLOG
BLOG