As interest in and integration of AI solutions surges, there is a pressing need for businesses to embark on initiatives that ensure the proper governance of AI design and use.
Inadequate governance of AI puts organizations at risk of non-compliance with regulatory requirements, compromising their decision-making process, and failing to meet customer expectations.
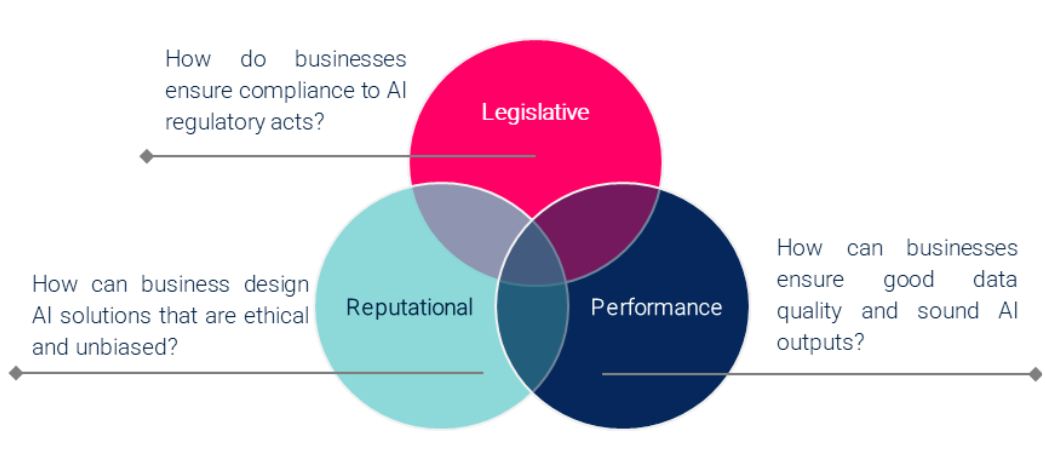
For example, a lack of understanding of the legislation governing AI can result in unintentional violations that can result in significant fines for businesses. Moreover, poorly managed data compromises data quality, which adversely affects the outputs of AI models and, consequently, decision-making and operational efficiency, ultimately causing financial losses.
Finally, using AI in situations without strong ethical considerations can damage a company’s credibility and create a trust gap with customers, such as using algorithms that unintentionally discriminate based on demographic data. Businesses must address these governance challenges to ensure the responsible and ethical use of AI, thereby safeguarding their operations and maintaining stakeholder trust.
“The AI Act outlines rules for data quality, transparency, human oversight, and AI accountability. At Artefact, we advise clients to follow seven imperatives to design compliant AI solutions.”Nawras Akroush, Data Strategy Consultant at Artefact NL
Emerging AI legislation: Regulating the use and adoption of AI for businesses
One of the most challenging aspects of AI governance is the ability of businesses to comply with regulations governing its use and implementation. The most notable of these regulations is the EU AI Act proposed by the European Commission in 2021. This act aims to establish clear requirements and obligations for AI developers, deployers, and users while easing administrative and financial burdens, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Although awaiting formal adoption by EU legislators, a provisional agreement has been reached, signaling its expected passage into law. Experts expect full adoption by mid-2024, with enforcement planned for early 2026.
The AI Act establishes rules for data quality, transparency, human oversight, and accountability of AI systems. It also establishes a framework for classifying the risk of AI systems based on their potential impact on health, safety, and fundamental human rights. The act defines four risk categories for AI solutions:
Artefact’s imperatives: Characteristics of a compliant AI solution
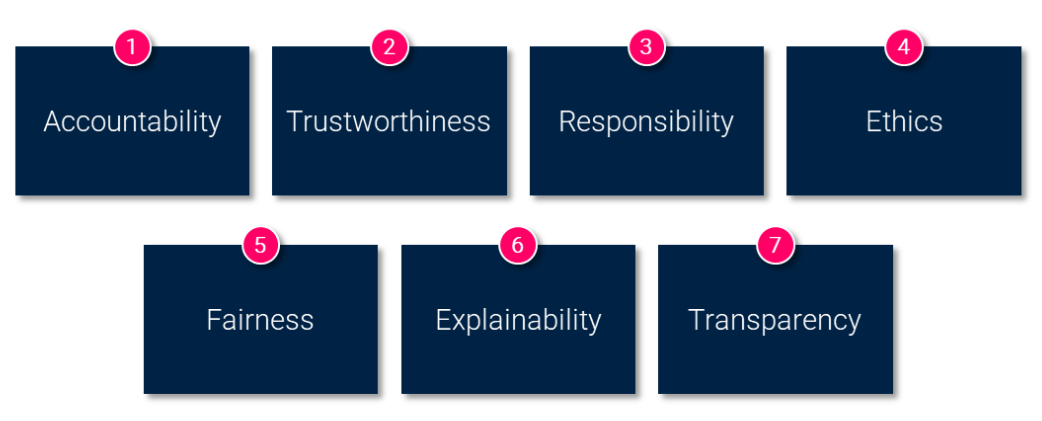
Based on the requirements of the EU AI Act and our experience in data and AI governance and compliance, we advise our clients to consider seven non-negotiable imperatives in any design or deployment of AI solutions:
To effectively develop and deploy AI solutions in line with these design imperatives and ensure proper AI governance to avoid legal, performance, and reputational risks, many companies will need to make significant organizational changes. These include:
Implementing change across all these organizational pillars can be a difficult and time-consuming process, so Artefact encourages businesses to begin developing and integrating AI governance frameworks. This will ensure compliance with future regulations and help meet customer expectations.
Urgent need: The importance of proactively adopting compliant AI solutions
In the dynamic world of AI technology, business leaders must take a proactive stance to position their organizations as leaders in responsible AI adoption. This will allow them to foster innovation while maintaining ethical obligations and regulatory compliance. In this era of rapid technological development and evolving regulations, a strategic and committed approach to AI governance will be a key element of sustainable success.
Want to learn more about navigating this issue? Stay tuned for part two of this series, where we’ll delve deeper into a framework businesses can use to establish proper AI governance within their organizations.

 BLOG
BLOG